Screen sequencers¶
A class responsible for the logic of the screen sequence. Works similarly to an iterator, returning the next screen when requested. The logic of the screen sequencer may or may not depend on the result of the previous screen.
Below is an example of a sequencer that returns a sequence of screens with some data that the user has to respond to (for example with a key press). If the user responds correctly, True is passed as the result, and the next returned screen is another screen with data. If the user responds incorrectly, False is passed as the result, and the next returned screen is a screen with a message. Then None is passed as the result to the message screen, and the next returned screen is another screen with data.
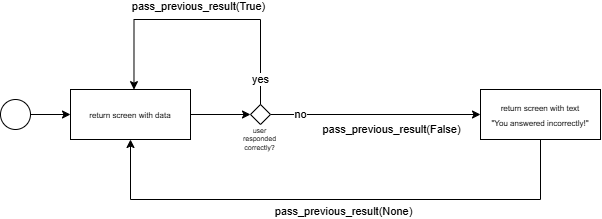
The methods must be called in the following order after initializing the sequencer:
1 call of
get_next()1 call of
pass_previous_result()go back to step 1 until the sequencer is finished
When the sequencer is finished, it raises StopIteration.
Interface¶
- class src.data_acquisition.sequencers.ScreenSequencer(*, logger: Logger | None = None)[source]¶
Bases:
Generic[T],ABC- get_next() EventfulScreen[T][source]¶
- Returns:
The next screen in the sequence.
- Raises:
IncorrectMethodCallOrderError – If the result of the previous screen was not provided (unless it’s the first screen).
StopIteration – If there is no next screen in the sequence.
How to subclass¶
Subclasses should implement the following methods:
_get_next() -> EventfulScreen[T]
Available properties and methods:
_previous_result: T: the result of the previous screen.